CMSIS-Cortex Microcontroller Software Interface Standard
The ARM® Cortex® Microcontroller Software Interface Standard (CMSIS) is a range of projects to help accelerate software development on ARM Cortex processors, and enable better collaboration of effort in the industry to accelerate new technologies.
The CMSIS enables consistent and simple software interfaces to the processor for interface peripherals, real-time operating systems, and middleware. It simplifies software re-use, reducing the learning curve for new microcontroller developers and cutting the time-to-market for devices.
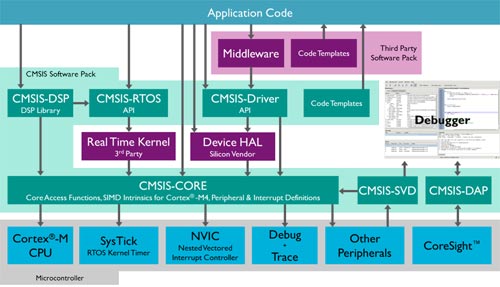
The CMSIS consists of the following components:
- CMSIS-CORE: API for the Cortex-M processor core and peripherals. It provides a standardized interface for Cortex-M0, Cortex-M0+, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M4, Cortex-M7, Cortex-M23, Cortex-M33, SC000, and SC300. Included are also SIMD intrinsic functions for Cortex-M4, Cortex-M7, and Cortex M33 SIMD instructions.
- CMSIS-Driver: Defines generic peripheral driver interfaces for middleware making it reusable across supported devices. The API is RTOS independent and connects microcontroller peripherals with middleware that can implement communication stacks and data storage, amongst others.
- CMSIS-DSP: DSP Library Collection with over 60 functions for various data types: fix-point (fractional q7, q15, q31) and single precision floating-point (32-bit). The library is available for Cortex-M0, Cortex-M0+, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M4, Cortex-M7, Cortex-M23 and Cortex-M33. The Cortex-M4, Cortex-M7, and Cortex-M33 implementations are optimized for the SIMD instruction set.
- CMSIS-RTOS API: Common API for real-time operating systems. It provides a standardized programming interface that is portable to many RTOS and enables therefore software templates, middleware, libraries, and other components that can work across supported the RTOS systems. It provides a standardized programming interface that is portable to many RTOS, enabling software templates, middleware, libraries, and other components that can work across all supported RTOS.
- CMSIS-Pack: Describes with a XML based package description (PDSC) file the user and device relevant parts of a file collection (called software pack) that includes source, header, and library files, documentation, Flash programming algorithms, source code templates, and example projects. Development tools and web infrastructures use the PDSC file to extract device parameters, software components, and evaluation board configurations.
- CMSIS-SVD: System View Description for Peripherals. Describes the peripherals of a device in an XML file and can be used to create peripheral awareness in debuggers or header files with peripheral register and interrupt definitions.
- CMSIS-DAP: Debug Access Port. Standardized firmware for a Debug Unit that connects to the CoreSight Debug Access Port. CMSIS-DAP is distributed as separate package and well suited for integration on evaluation boards. This component is provided as separate download.
(https://github.com/ARM-software/CMSIS_5)
(http://arm-software.github.io/CMSIS_5/General/html/index.html)
CMSIS-CORE gives the user access to the processor core and the device peripherals. It defines:
- Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) for Cortex-M processor registers with standardized definitions for the SysTick, NVIC, System Control Block registers, MPU registers, FPU registers, and core access functions.
- System exception names to interface to system exceptions without having compatibility issues.
- Methods to organize header files that makes it easy to learn new Cortex-M microcontroller products and improve software portability. This includes naming conventions for device-specific interrupts.
- Methods for system initialization to be used by each MCU vendor. For example, the standardized SystemInit() function is essential for configuring the clock system of the device.
- Intrinsic functions used to generate CPU instructions that are not supported by standard C functions.
- A variable to determine the system clock frequency which simplifies the setup the SysTick timer.
CMSIS-CORE files:
<device>.h
system_<device>.h
core_<cpu>.h
startup_<device>.s
<device> is replaced with the specific device name or device family name; i.e. stm32f401xe,
<cpu> is replaced with MCU’s Core shortcut; i.e. cm0 (Cortex M0), cm4 (Cortex M4).
- <device>.h– contains device specific informations: interrupt numbers (IRQn) for all exceptions and interrupts of the device, definitions for the Peripheral Access to all device peripherals (all data structures and the address mapping for device-specific peripherals). It also provide additional helper functions for peripherals that are useful for programming of these peripherals.
- **core\<cpu>.h**_– defines the core peripherals and provides helper functions that access the core registers (SysTick, NVIC, ITM, DWT etc.).
- **startup\<device>.s**_– startup code and system configuration code (reset handler which is executed after CPU reset, exception vectors of the Cortex-M Processor, interrupt vectors that are device specific).